👷 Note for Homeowners & DIYers: Hotian Windows is a wholesale custom manufacturer for commercial and residential projects. We supply complete door systems (frame + slab + hardware) to builders and distributors. We do not sell individual replacement parts (like hinges, jambs, or seals) to the public.
- Are you a builder? [View our Door Catalog]
- Need Technical Specs? [Jump to Specifications] (Anchor link to bottom)
Understanding the anatomy of a door is critical for specifying the right product for high-performance buildings. Whether you are designing a commercial storefront or a luxury villa, the quality of components—from the thermal break in the frame to the multi-point locking system—determines the longevity of the project.
The Door Frame System (Structural Anatomy)
Manufacturer’s Insight: The frame is not just a border; it is the structural interface between the building envelope and the fenestration unit. In commercial projects, frame failure is 3x more common than panel failure due to inadequate wall thickness specifications.
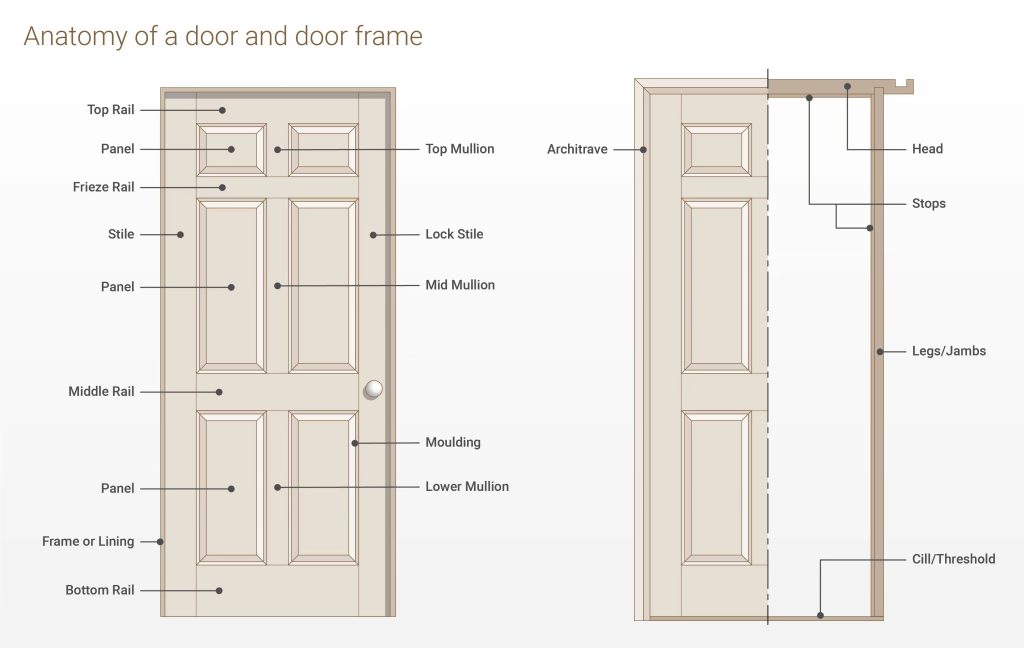
The frame (or jamb) is the interface between the building structure and the door leaf. In 2026 commercial standards, a simple wooden frame is often insufficient. High-performance aluminum frames are the industry standard for durability.
A. Head & Side Jambs (The Profile System)
The Head is the horizontal top member, and the Jambs are the vertical sides.
- The DIY View: It’s just the border holding the door.
- The Professional Spec: The wall thickness of the aluminum profile determines the door’s structural integrity. Standard market doors often use 1.2mm – 1.4mm aluminum.
- Hotian Advantage: For our commercial entrance systems, we utilize 2.0mm – 3.0mm thick thermal break aluminum profiles. This prevents frame distortion under heavy wind loads or when supporting oversized glass units (up to 3 meters high).
- 👉 Designing a heavy-duty entrance? View our [Commercial Aluminum Door Series].
B. Thermal Break (The Energy Shield)
- What it is: You will see a black strip crimped between the interior and exterior aluminum profiles. This is the Polyamide (PA66) Thermal Break.
- Why it matters: Aluminum is a conductor. Without this break, the frame acts as a “thermal bridge,” transferring outdoor cold/heat inside.
- Engineering Detail: We use PA66 GF25 (25% glass fiber reinforced nylon) strips. In our Passive House series, these strips are up to 34mm wide, significantly lowering the U-value to meet strict energy codes (Energy Star / NFRC).
👉 Need U-value reports for your project? [Contact Our Engineering Team].
C. Threshold & Sill (Water Management)
The bottom component of the frame is critical for weatherproofing.
- High-Step Threshold: Offers the best water tightness (high Pascal rating) for exterior doors exposed to direct rain.
- Flush Sill (Zero Threshold): Essential for modern aesthetics and ADA compliance (wheelchair access).
- The Challenge: Flush sills notoriously leak water.
- The Solution: Hotian employs a “Hidden Drain” subsystem. We engineer a sub-sill drainage channel that sits below the floor level, allowing for a seamless, flush look while capturing and diverting water away from the building foundation.
D. Architrave & Brickmold (The Integration)
These are the exterior trim components that seal the gap between the window frame and the building facade (cladding, brick, or siding).
- Nailing Fin: For US markets, we provide integral Nailing Fins for easy installation in wood-frame construction.
- Brickmold: For renovation projects or masonry openings, our snap-on brickmolds provide a clean finish without messy wet sealing.
Door Panel Components
The “Sash” (or leaf) is the operational element of the door. While residential doors often use simple slab construction, high-performance architectural doors are engineered assemblies designed for rigidity and insulation.
A. Stiles & Rails (Sash Construction)
- Definition: Stiles are the vertical structural members; Rails are the horizontal ones.
- The Weak Point: In cheap aluminum doors, stiles and rails are connected with simple screws. Over time, gravity causes the sash to sag (drag on the floor).
B. The Glazing System (Glass Specs)
Glass typically occupies 80% of a door’s surface area, making it the biggest factor in thermal performance.
- IGU (Insulated Glass Unit): We standardly offer Double Glazing (5mm+12A+5mm) but recommend Triple Glazing for cold climates.
- Warm Edge Spacers (TGI): Instead of conductive aluminum spacers, we use composite “Warm Edge” spacers between glass panes to prevent condensation at the glass edges.
- Low-E Coatings: Soft-coat Low-E (Low-Emissivity) layers are applied to reflect infrared heat—keeping heat inside during winter and outside during summer.
- Option: Switchable Privacy Glass (Smart Glass) is available for luxury hotel or office projects.
C. Glazing Bead (Security & Aesthetics)
- Definition: The aluminum strip that snaps into the sash to hold the glass unit in place.
- Security Feature: For commercial projects, we spec Internal Glazing Beads. This means the glass can only be removed from the inside of the building, preventing burglars from removing the glass pane from the exterior.
- Design Profile: Available in Square (Modern), Beveled (Traditional), or Sloped designs to match the building’s architectural style.
D. Mullions (Structural Dividers)
- Definition: Vertical or horizontal bars that divide the sash into smaller lites.
- SDL vs. TDL:
- SDL (Simulated Divided Lite): Grids adhered to the glass surface for a classic look with modern thermal performance.
- TDL (True Divided Lite): Actual profiles separating individual glass units (stronger but more expensive).
👉 Architects: We can customize mullion patterns to match historic renovation requirements.
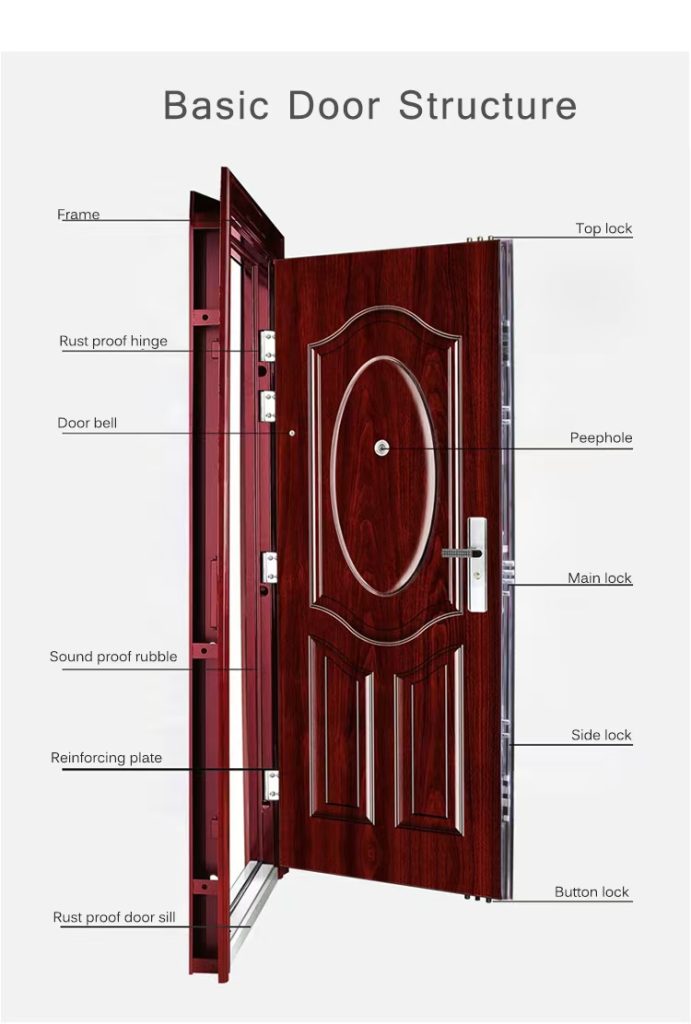
Door Panel Components
This is the part you actually swing, slide, or fold! The “door slab.”
Door Hardware Components: The Functional Bits)
A door is only as good as its hardware. In commercial applications, hardware failure is the #1 cause of maintenance calls. We partner with global leaders (Siegenia, Hoppe, CMECH, Sobinco) to ensure Class-5 operation durability..
Door Hardware Components
A. Hinge Systems (The Load Bearers)
- Butt Hinges (Standard): Common in residential wood doors.
- 3D Adjustable Hinges (Commercial): Our standard for aluminum doors. These allow installers to adjust the door sash in three dimensions (Up/Down, Left/Right, In/Out) with an Allen key, ensuring perfect alignment years after installation.
- Concealed Hinges: Completely hidden within the frame for a minimalist, clean aesthetic. Capable of supporting 150kg+ heavy-duty sashes.
B. Multi-Point Locking System
- VS Single Deadbolt: A standard deadbolt locks at one point. It’s easy to pry open.
- The Multi-Point Solution: When the handle is lifted, our transmission gear engages locking points (mushroom cams or hooks) at the top, center, and bottom of the door simultaneously.
- Benefits:
- Security: Meets RC3 Anti-Burglary standards.
- Sealing: Compresses the sash tightly against the weatherstripping along the entire height, eliminating drafts.
C. Gaskets & Weatherstripping (EPDM)
- Material Matters: We do not use PVC rubber, which cracks in sunlight. We use EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) automotive-grade composite sealing strips.
- Co-Extruded Seals: Our seals often feature a multi-chamber design to improve sound insulation (STC rating) and water tightness.
Special Door Types & Unique Components
Different door styles have unique parts:
Special Door Styles & Components
- A. French Door Anatomy: Wondering what is french door? It’s typically a pair of doors with glass panels (lites) that swing open from the middle. Unique parts include:
- Astragal: A vertical molding strip attached to the edge of one door in a pair. It covers the gap between the two doors when closed, providing a seal and sometimes housing locking mechanisms.
- Multipoint Locks: Locking systems that secure the door at multiple points (top, bottom, middle) with a single handle operation, common on taller French doors or patio doors for security and sealing.
- Flush Bolts: As mentioned before, used to secure the inactive door.
- B. Sliding, Pocket, Barn, and Bi-fold Doors: These rely on tracks and rollers instead of hinges.
- Track Systems: Metal or plastic channels (mounted overhead or sometimes at the floor) that guide the door’s movement.
- Hangers/Rollers: Wheels or carriers attached to the top of the door panel that ride in the track.
- Guides: Small pieces (often floor-mounted) that keep the bottom of sliding/barn doors from swinging side-to-side.
- Pocket Frames: Special pre-fabricated wall structures designed to hold a pocket door neatly inside the wall when open.
- Edge Pulls: Small, recessed pulls used on the edge of pocket doors to retrieve them from the wall cavity.
- Pivot/Align Hardware: Special connectors and pivots used in bi-fold doors to allow panels to fold smoothly and stay aligned.
Door Measurements & Specifications: The Numbers Game
Getting the details right is crucial for proper function.
- A. Standard Sizes: Doors come in common sizes. Knowing the standard door sizes (like 80″ height and widths like 30″ or 36″ in the US) helps when ordering or replacing. Metric sizes are used in many other parts of the world.
- B. Hardware Positioning:
- Backset: The distance from the edge of the door to the center of the hole bored for the lockset (common backsets are 2 ⅜” and 2 ¾”). Critical for ensuring the lock fits correctly.
- Bore Size: The diameter of the main hole(s) drilled for the lockset/deadbolt. Needs to match the hardware requirements.
- Hinge Spacing & Gap: Hinges need to be placed correctly along the jamb and door edge. Small, consistent gaps around the door panel are needed for it to swing freely without binding.
- C. Installation Tolerances: There are acceptable ranges for gaps and clearances around the door and frame to allow for smooth operation and seasonal wood movement. Building codes might specify certain clearances, especially for fire doors.
- D. Ratings & Standards:
- ANSI/BHMA: Look for grades (like Grade 1, 2, 3) on hardware indicating performance, durability, and security standards set by the American National Standards Institute / Builders Hardware Manufacturers Association. Grade 1 is typically the highest/most durable.
- Fire Ratings: Doors (and frames/hardware) used in specific locations (like between garage and house) need fire ratings (e.g., 20-minute, 90-minute) indicating how long they resist fire.
- Sound Ratings (STC): Sound Transmission Class ratings indicate how well a door assembly blocks sound. Higher STC means better soundproofing.
Accessibility & Specialized Components: Meeting Specific Needs
Some components are designed for specific requirements:
- A. ADA-Compliant Features: To meet accessibility standards:
- Lever handles are required instead of round knobs (easier to grip).
- Thresholds must be low profile (max ½ inch high, often beveled).
- Door closers must operate slowly enough not to hinder passage.
- Minimum clear opening width (usually 32 inches) must be provided.
- B. Fire & Sound Control:
- Intumescent Seals: Special strips applied to fire-rated doors/frames that swell rapidly when exposed to heat, sealing the gaps to block smoke and flames.
- Fire-Rated Glass: Glass that has been tested to withstand fire for a specific period.
- Acoustic Cores: Dense materials inside the door panel designed to block sound.
- Acoustic Seals & Sweeps: High-performance seals around the frame and bottom of the door specifically designed for maximum sound reduction.
- C. Energy Efficiency:
- Insulated Cores: Foam or other insulating materials inside the door panel (especially important for exterior doors) to reduce heat transfer (measured by R-value or U-factor).
- High-Performance Weatherstripping & Sweeps: Ensure tight seals to prevent air leakage.
Troubleshooting by Component: Fixing Common Problems
Knowing the parts helps diagnose issues:
- “My door sticks or binds.”
- Check: Hinges (loose screws, bent pins, worn out?), Door Panel (swollen from humidity?), Frame (settling, out of square?).
- Solution: Tighten screws, shim hinges, plane door edge slightly, adjust frame if possible.
- “The door won’t latch properly.”
- Check: Latch Bolt alignment with Strike Plate hole, Strike Plate position, Hinge alignment (sagging door?).
- Solution: Adjust strike plate position (file opening wider or reposition), shim hinges to re-align door.
- “It’s drafty around the door.”
- Check: Weatherstripping (worn, compressed, missing?), Door Sweep (worn, damaged, poor contact?), Door Stops (is the door closing tightly against them?).
- Solution: Replace weatherstripping/sweep, adjust stops or latch for a tighter close.
- “The lock is hard to turn or sticks.”
- Check: Key worn? Lock mechanism need lubrication? Bolt misaligned with strike plate?
- Solution: Try graphite lubricant (not oil!), check alignment, may need lockset replacement.
DIY vs. Replace: Simple adjustments (tightening screws, lubricating, replacing weatherstripping) are often DIY. More complex issues (planing doors, repositioning strike plates significantly, replacing mortise locks) might need more skill or professional help.
Selecting the Right Door Components: Making Smart Choices
When buying or upgrading, consider:
- A. Materials & Durability: Compare wood, fiberglass, steel, composite based on your climate, budget, and desired maintenance level. (Refer back to Section IV.B and linked guides). How long do you need it to last? How much wear will it get?
- B. Matching Styles: Choose panel designs, hardware finishes, and casing styles that complement your home’s architecture (Traditional, Modern, Farmhouse, etc.). Consistency matters!
- C. Functionality, Performance, & Energy Efficiency:
- Security: Prioritize strong deadbolts, solid core or metal doors for exterior access.
- Sound Control: Opt for solid core doors and good seals between rooms if noise is a concern.
- Energy Savings: Crucial for exterior doors – look for insulated cores and excellent weatherstripping/sweeps.
- Ease of Installation: Considering a What is a Pre-Hung Door? unit (door already in its frame) can save significant installation time and effort compared to installing a slab door.
Comprehensive Glossary of Door Terminology
We’ve covered a lot of terms! This whole guide acts as a glossary, but here are a few key ones recapped:
- Jamb: The vertical side parts of the door frame.
- Stile: The vertical structural edge pieces of the door panel itself.
- Rail: The horizontal structural pieces of the door panel.
- Stop: The strip inside the frame that the door closes against.
- Casing: The decorative trim around the frame.
- Strike Plate: The metal plate on the jamb that catches the latch/bolt.
- Backset: Measurement from door edge to center of lock hole.
- Pre-Hung: A door unit sold with the panel already mounted in the frame.
- Slab: Just the door panel itself, without frame or hardware.
Conclusion & Additional Resources
And there you have it! A deep dive into the world of door parts. See? Not so scary!
Key Takeaways:
- A door is a system: Frame, Panel, Hardware, and Decorative parts all work together.
- Knowing the names of parts (like stiles, rails, jambs, strike plates) helps you understand how doors work, fix problems, and choose wisely.
- Materials (wood, fiberglass, steel), core type (solid/hollow), and hardware quality significantly impact performance, durability, and security.
- Special doors (French, sliding, etc.) have unique components you need to know about.
- Measurements and specifications (like backset and standard sizes) are critical for proper fit and function.
Understanding these components empowers you to maintain your home better, make informed decisions during renovations, and appreciate the clever engineering in something as simple as a door!
Hopefully, this guide has opened the door (pun intended!) to a better understanding of all those essential parts. Good luck with your next door project!










