Windows play a crucial role in the energy efficiency of your home. They are not just aesthetic elements that allow light and air into your living space; they are also vital in regulating temperature, reducing energy consumption, and improving indoor comfort.
In fact, heat gain and loss through windows account for 25%–30% of residential heating and cooling energy use.
Choosing the right energy-efficient windows can significantly reduce this energy loss, saving you money and making your home more comfortable year-round. This comprehensive guide will help you understand the key aspects of energy-efficient windows, including their benefits, how they work, what to look for when buying them, and how to maximize their efficiency.
What Are Energy-Efficient Windows?
Energy-efficient windows are designed to prevent heat transfer between the inside and outside of your home. They do this by using advanced technologies such as multiple panes of glass, special coatings, and insulating gas fills. These features help maintain a consistent indoor temperature by reducing heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer.
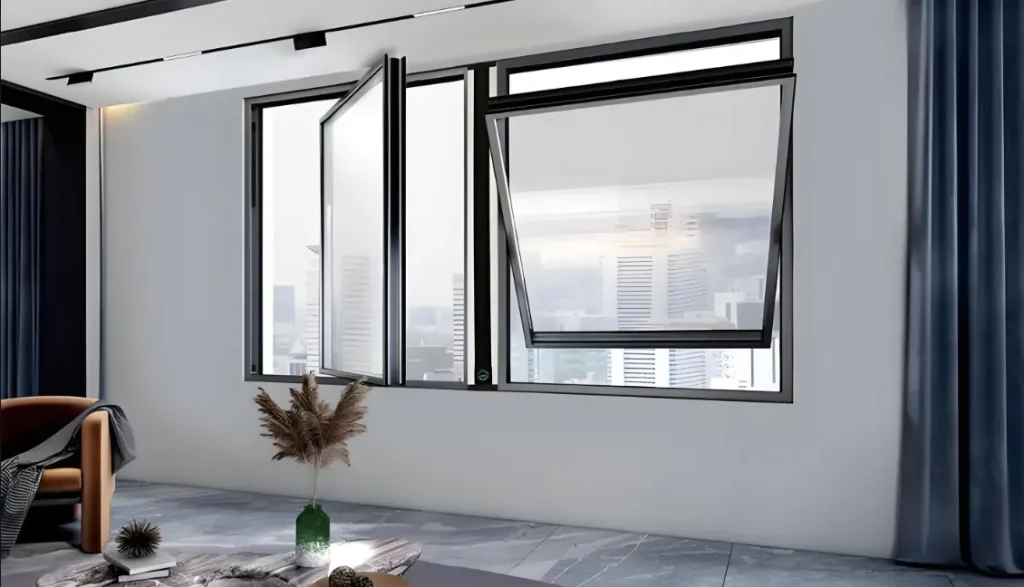

Key Components of Energy-Efficient Windows
- Glass (Glazing)
- Double-Pane or Triple-Pane Glass: These windows have two or three layers of glass with air or gas-filled spaces between them. The extra layers provide better insulation compared to single-pane windows.
- Low-Emissivity (Low-E) Coatings: This invisible metallic coating on the glass reflects infrared light, keeping heat inside during winter and outside during summer.
- Gas Fills: Argon or krypton gas is often used between panes to improve insulation. These gases are denser than air, reducing heat transfer.
- Frame Materials
- Vinyl: Known for its excellent insulation properties and low maintenance, vinyl frames are a popular choice for energy-efficient windows.
- Wood: Wood frames offer good insulation but require more maintenance than vinyl or fiberglass.
- Fiberglass: Strong and durable, fiberglass frames provide excellent thermal performance similar to wood but with less maintenance.
- Sealing and Spacers
- Proper sealing around the window frame is essential to prevent air leaks. High-quality spacers between panes also reduce heat transfer by maintaining the correct distance between glass layers.
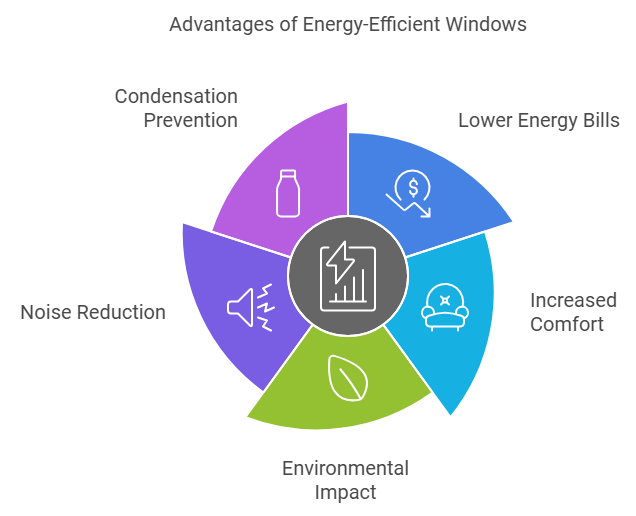
Benefits of Energy-Efficient Windows
Energy-efficient windows offer numerous advantages that go beyond just saving energy. Here are some key benefits:
1. Lower Energy Bills
By reducing heat loss in winter and limiting heat gain in summer, energy-efficient windows lower the demand on your heating and cooling systems. This can lead to savings of 7%–15% on annual energy bills. Additionally, homes with ENERGY STAR® certified windows can save up to 12% on heating and cooling costs annually.
2. Increased Comfort
Energy-efficient windows help maintain a consistent indoor temperature by reducing drafts and cold spots near windows. In winter, they keep the warmth inside; in summer, they block excessive heat from entering. This results in a more comfortable living environment year-round.
3. Environmental Impact
By using less energy to heat or cool your home, you reduce your carbon footprint. Energy-efficient windows can cut energy consumption by up to 25%, which translates into significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions. This makes them an eco-friendly choice for environmentally conscious homeowners.
4. Noise Reduction
The multiple layers of glass and tight seals found in energy-efficient windows also help reduce noise pollution from outside sources such as traffic or noisy neighbors. This is especially beneficial if you live in a busy urban area.
5. Condensation Prevention
Energy-efficient windows are less prone to condensation because they maintain a higher surface temperature on the interior side of the glass. This reduces the risk of mold growth and damage caused by moisture buildup.
How Do Energy-Efficient Windows Work?
Energy-efficient windows work by minimizing heat transfer through several mechanisms:
- Insulation: Multiple panes of glass with gas fills act as barriers to slow down the movement of heat.
- Reflecting Heat: Low-E coatings reflect infrared light (heat) back into the home during winter while reflecting it away during summer.
- Sealing: Properly sealed window frames prevent drafts and air leaks that can undermine the efficiency of your heating or cooling system.
Key Metrics for Measuring Efficiency
When shopping for energy-efficient windows, it’s important to understand certain ratings that indicate their performance:
| Metric | Description | Ideal Value |
|---|---|---|
| U-Factor | Measures how well a window prevents heat from escaping (lower is better). | ≤ 0.22 for colder climates |
| Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) | Measures how well a window blocks solar heat (lower is better). | ≤ 0.23 for warmer climates |
| Visible Transmittance (VT) | Indicates how much visible light passes through the window. | Higher values allow more light |
| Air Leakage (AL) | Measures how much air passes through cracks in the window assembly. | Lower values indicate better sealing |
Types of Energy-Efficient Windows
There are several types of energy-efficient windows available, each with its own advantages depending on your needs:
1. Fixed Windows
Fixed or picture windows do not open or close, making them highly efficient because there are no moving parts where air could leak through. However, they lack ventilation capabilities.
2. Casement Windows
Casement windows have hinges on one side and open outward like a door. They create a tight seal when closed, making them one of the most efficient operable window types.
3. Awning Windows
Awning windows are hinged at the top and open outward from the bottom. Like casement windows, they provide excellent sealing when closed.
4. Double-Hung Windows
These windows have two sashes that slide vertically past each other within the frame. While convenient for ventilation, double-hung windows tend to be less efficient than casement or awning styles due to potential air leakage around moving parts.
5. Sliding Windows
Sliding windows move horizontally along tracks but may not seal as tightly as other types like casement or fixed windows.
What to Consider Before Buying Energy-Efficient Windows
Choosing new or replacement energy-efficient windows involves several important considerations:
1. Climate
Your geographic location plays a major role in determining which type of window will be most effective for your home’s needs:
- In colder climates, prioritize low U-factor ratings to minimize heat loss.
- In warmer climates, focus on low SHGC ratings to reduce solar heat gain.
- For temperate climates with hot summers and cold winters, look for windows with both low U-factors and SHGCs.
2. Window Placement
Windows facing different directions receive varying amounts of sunlight throughout the day:
- South-facing windows benefit from Low-E coatings that block UV rays while allowing natural light.
- North-facing windows should prioritize insulation over solar control since they receive less direct sunlight.
3. Frame Material
Different frame materials offer varying levels of insulation:
- Vinyl is affordable and provides excellent insulation.
- Fiberglass is durable with good thermal performance but tends to be more expensive.
- Wood offers great insulation but requires regular maintenance against moisture damage.
4. Installation Quality
Even the best-performing window will fail if it’s not installed correctly! Ensure that your installer follows best practices such as proper sealing around frames to prevent drafts or water infiltration.
Cost vs Savings: Is It Worth It?
Energy-efficient windows typically cost more upfront than standard ones due to their advanced materials and construction techniques:
- On average, replacing single-pane windows with ENERGY STAR-certified models can save homeowners $126–$465 per year depending on their location.
- The return on investment (ROI) for energy-efficient window installation is high because it not only reduces utility bills but also increases property value by improving curb appeal and comfort levels inside your home.
Additionally, homeowners may qualify for tax credits or rebates when installing ENERGY STAR-certified products, further offsetting initial costs.
Maximizing Window Efficiency
To get the most out of your new energy-efficient windows:
- Ensure proper installation by hiring certified professionals who follow manufacturer guidelines.
- Use window treatments like blinds or curtains strategically. Open them during sunny winter days for passive heating; close them during hot summer afternoons.
- Regularly inspect seals around window frames for any signs of wear and tear that could lead to air leaks.
- Consider adding storm shutters if you live in an area prone to extreme weather conditions like hurricanes or heavy snowfall.
Conclusion
Investing in energy-efficient windows is one of the smartest decisions you can make as a homeowner. Not only will you save money on utility bills but also enjoy increased comfort throughout every season while reducing your environmental impact. When selecting new or replacement windows:
- Look for ENERGY STAR® certification.
- Pay attention to U-factor & SHGC ratings suitable for your climate zone.
- Choose durable frame materials like vinyl or fiberglass depending on budget & maintenance preferences.
By understanding these factors before buying energy-efficient windows tailored specifically towards optimizing performance based on regional climate conditions, you’ll be well-equipped to make informed decisions benefiting both wallet & planet alike!