أهلاً! هل فكرتَ يومًا في كل الأجزاء التي تُكوّن الباب؟ ربما لا، أليس كذلك؟ إنه يُفتح ويُغلق فحسب! لكن فهم أجزاء الباب المختلفة - تشريح، إذا صح التعبير – فهو في الواقع مفيد للغاية.
لماذا هذا مهم؟ حسنًا، معرفة الأجزاء تساعدك على:
- اختر الباب المناسب: سواء كنت تشتري منتجًا جديدًا أو تستبدله، فستعرف الميزات التي يجب البحث عنها.
- صيانة أبوابك: إن اكتشاف التآكل على جزء معين يعني أنه يمكنك إصلاح المشكلات الصغيرة قبل أن تتحول إلى مشكلات كبيرة.
- التثبيت أو الترقية: إن معرفة أسماء الأجزاء تجعل التعليمات أكثر وضوحًا وتساعدك على التواصل مع المحترفين أو موظفي متجر الأجهزة.
- استكشاف المشاكل وإصلاحها: هل بابك عالق؟ هل يتسرب منه تيار هواء؟ هل لا يُغلق بإحكام؟ معرفة الأجزاء تُساعد في تحديد السبب.
هذا الدليل مُوجّه للجميع - أصحاب المنازل الراغبين في القيام ببعض الأعمال بأنفسهم، والبنائين الذين يحتاجون إلى مرجع واضح، والمُجدّدين الذين يُخططون للتجديدات. سنتناول كل ما يتعلق بالأبواب القياسية، والأنماط الحديثة، والأنواع الخاصة كالأبواب الفرنسية أو المنزلقة، والإطار الذي يُثبّتها، وجميع الأدوات الأساسية. هل أنت مستعد لتصبح خبيرًا في الأبواب؟ هيا بنا!
نظرة عامة على تشريح الباب
تخيّل مدخلًا متكاملًا. إنه أكثر من مجرد لوح خشبي أو معدني تدفعه! إنه نظام متكامل يعمل معًا.
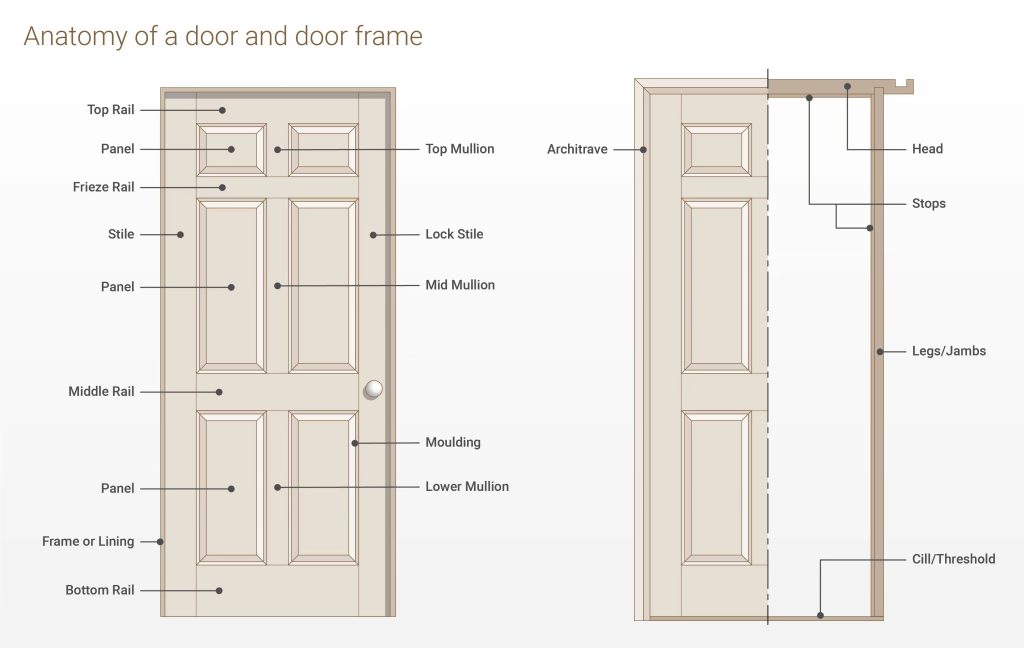
لتبسيط الأمر، دعنا نقوم بتجميع المكونات الرئيسية:
جدول مرجعي سريع: مجموعات المكونات الرئيسية
| مجموعة | ما يتضمنه | الوظيفة الرئيسية |
|---|---|---|
| إطار الباب | الرأس، العتبات، العتبة/العتبة، التوقفات | يحمل الباب ويوفر الدعم الهيكلي |
| لوحة/لوح الباب | الأعمدة، القضبان، الألواح، القلب (صلب/مجوف) | الجزء المتحرك الفعلي من الباب |
| الأجهزة | المفصلات، الأقفال، المقابض، الغلقات، لوحات الركل، وما إلى ذلك. | يسمح بالحركة والأمان والوظيفة |
| ديكوري | التغليف/التشطيب، العتب، تصميمات الألواح، التشطيبات | يضيف الأناقة، ويغطي الفجوات، ويعزز المظهر |
تخيل الأمر كما لو كان جسدك: الإطار هو الهيكل، واللوحة هي الجسم الرئيسي، والأجزاء المعدنية هي مفاصلك ويديك التي تسمح بالحركة والتفاعل، والأجزاء الزخرفية هي الملابس والأناقة! يجب أن تتكامل هذه الأجزاء بسلاسة ليعمل الباب بشكل صحيح. يبدو الأمر بسيطًا، أليس كذلك؟ لكن التفاصيل مهمة!
مكونات إطار الباب: نظام الدعم
الإطار هو الهيكل الأساسي المُدمج في فتحة الجدار التي تحمل لوحة الباب. لنبدأ بشرحه:
أ. العناصر الهيكلية (العظام!)
- الرأس/الرأس: هذه هي القطعة الأفقية العلوية للإطار، وتقع فوق الباب مباشرةً.
- العتبات: هاتان هما القطعتان الجانبيتان الرأسيتان للإطار.
- مفصلات الباب: الجانب الذي يتم فيه تثبيت المفصلات.
- دعامة الضرب (أو دعامة القفل): الجانب الذي يدخل فيه مزلاج/مسامير القفل إلى لوحة الضربة.
- عتبة/عتبة: هذه هي القطعة الأفقية السفلية للإطار، والتي توجد بشكل أساسي في الخارج الأبواب. تُثبّت على الأرضية وتساعد على عزل أسفل الباب ضد العوامل الجوية والتيارات الهوائية. عادةً ما لا تحتوي الأبواب الداخلية على عتبة هيكلية، بل أرضية فقط تحتها.
- سدادات الأبواب: هذه شرائح رقيقة من الخشب أو المعدن تُثبّت على السطح الداخلي للرأس والعتبات الجانبية. وظيفتها بالغة الأهمية: فهي تمنع الباب من التأرجح. خلال الإطار وتوفير سطح للباب للراحة عليه عند إغلاقه، مما يساعد على إنشاء ختم.
ب. أجزاء الإطار الزخرفية والوظيفية (اللمسات النهائية)
- الغلاف/التشطيب: هذا هو القالب الزخرفي المثبت حول الخارج حافة إطار الباب، تغطي الفجوة بين الإطار والجدار الجبس. يضفي مظهرًا نهائيًا.
- قالب الطوب: مشابه للغلاف، ولكن يستخدم عادة على الخارج جانب إطارات الأبواب الخارجية. غالبًا ما يكون أكثر سمكًا، ومُصممًا لتوفير سطحٍ للألواح الجانبية أو الطوب، مما يوفر حمايةً أفضل من العوامل الجوية.
- عتب: هذا هو في الأساس نوع أكثر فخامة وتفصيلاً من الغلاف، والذي غالبًا ما يتم بناؤه من قطع متعددة من القوالب للحصول على مظهر معماري أكثر روعة.
- مانع تسرب الهواء: هذا مانع تسرب مرن (مصنوع من الإسفنج، أو المطاط، أو الفينيل، إلخ) يُثبّت على إطار الباب (غالبًا في أخدود في عتبات الأبواب أو على مصداتها)، أو أحيانًا على حافة الباب نفسها. وظيفته الرئيسية هي منع تيارات الهواء والماء والضوضاء عند إغلاق الباب. وهو بالغ الأهمية لكفاءة الطاقة، وخاصةً في الأبواب الخارجية!
- كنس الباب: عادة ما تكون متصلة بـ الحافة السفلية للوحة الباب في حد ذاته، يُعدّ الكَنس شريطًا (غالبًا ما يكون مصنوعًا من الفينيل أو زعانف الفرشاة) يُغلق الفجوة بين أسفل الباب والعتبة/العتبة أو الأرضية. عامل أساسي آخر في منع تيارات الهواء!
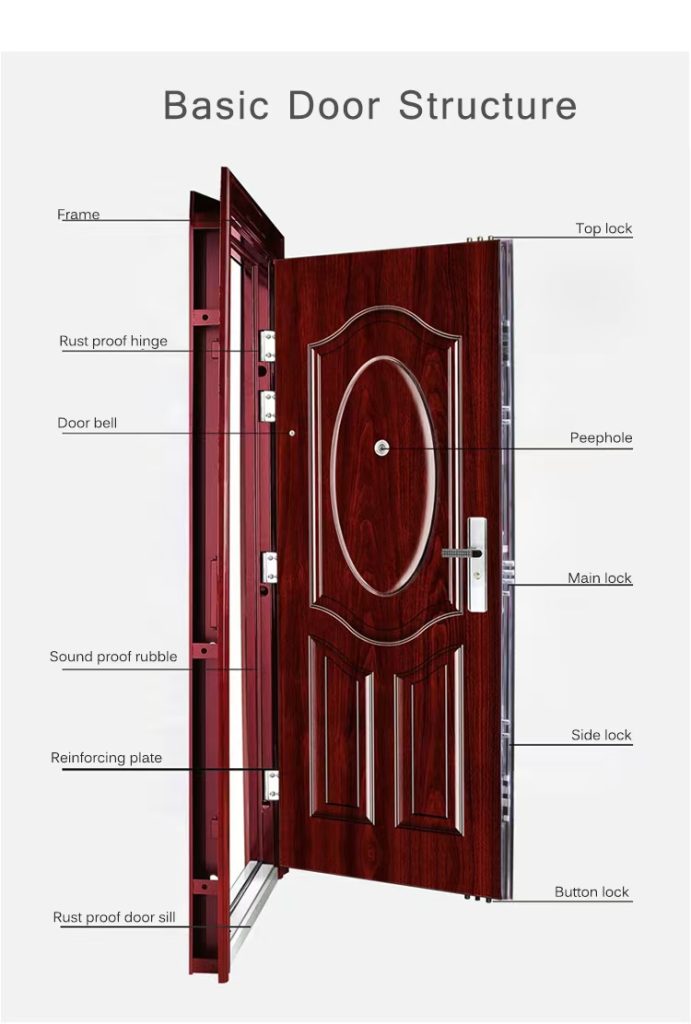
مكونات لوحة الباب
هذا هو الجزء الذي يمكنك تحريكه أو تحريكه أو طيه! "لوح الباب".
مكونات لوحة الباب
هذا هو الجزء الذي يمكنك تحريكه أو تحريكه أو طيه! "لوح الباب".
أ. البنية الداخلية (ما هو الموجود بالداخل؟)
فكر في باب اللوحة الخشبية التقليدي مثل إطار الصورة:
- ستايلز: هذه هي القطع الهيكلية الرأسية الرئيسية على الحواف اليمنى واليسرى للوحة الباب.
- نمط القفل: العمود الذي يتم فيه تثبيت مجموعة القفل (المقبض/الفتحة/القفل).
- نمط المفصلة: العمود الذي يتم فيه تثبيت المفصلات.
- القضبان: هذه هي القطع الهيكلية الأفقية.
- السكة العلوية: القطعة الأفقية العلوية.
- السكة السفلية: القطعة الأفقية الأدنى (غالبًا ما تكون أوسع لتحقيق الاستقرار والتشذيب).
- السكة الوسطى (أو السكة المتقاطعة / السكة المقفلة): قطع أفقية تقع بين القضبان العلوية والسفلية، غالبًا على ارتفاع القفل، وتقسم الباب إلى ألواح.
- الألواح: هذه هي الأجزاء الكبيرة، الرفيعة عادةً، المسطحة أو المرتفعة التي تملأ الفراغات بين الأعمدة والدرابزين. يمكن أن تكون مصنوعة من الخشب، أو ألواح MDF، أو الزجاج، إلخ.
- الموليونز (أو المونتين): وهي عبارة عن قطع أصغر عمودية أو أفقية تعمل على تقسيم لوحة الباب إلى عدة ألواح أو ألواح زجاجية أصغر حجمًا (ليتس).
ب. المواد وأنواع الألواح (مما هي مصنوعة؟)
تأتي ألواح الأبواب بمواد مختلفة، ولكل منها إيجابيات وسلبيات:
- خشب: كلاسيكي، جميل، قابل للصبغ أو الطلاء. أنواع مختلفة توفر مظهرًا ومتانة متفاوتة. هل تحتاج مساعدة في الاختيار؟ اطلع على الأدلة على أفضل أنواع الخشب للأبواب الخارجية أو ما هو أفضل نوع من الخشب للأبواب الداخلية؟.يمكنك حتى تسوق بابنا الخشبي اختيار الأفكار.
- معدن: في كثير من الأحيان الفولاذ أو الألومنيوم (ما هو الباب الألومنيوممتين وآمن، ويُستخدم غالبًا للأبواب الخارجية. قابل للطلاء. الفولاذ قابل للتآكل أو الصدأ إذا لم يُصان جيدًا؛ أما الألومنيوم فهو أخف وزنًا ومقاوم للصدأ.
- الألياف الزجاجية: متين، سهل الصيانة، موفر للطاقة. يُحاكي مظهر عروق الخشب. مقاوم للخدوش والعفن والتشوهات بشكل ممتاز. غالبًا ما يكون خيارًا رائعًا - تعرّف على المزيد حول ما هي أفضل مادة للباب الأمامي.
- مركب: هذه الأبواب (ما هو الباب المركبتُصنع هذه الألواح باستخدام مواد متعددة (مثل ألياف الخشب والبلاستيك والراتنجات) مضغوطة معًا، وغالبًا ما تكون ذات غلاف خارجي متين. تتميز هذه الألواح بقوة وعزل جيدين ومقاومة للعوامل الجوية.
- زجاج: تُستخدم للألواح (الألواح الخفيفة) داخل الأبواب (مثل الأبواب الفرنسية) أو في بعض الأحيان كمادة أساسية (أقل شيوعًا في أبواب المرور القياسية).
أنواع النواة مهمة أيضًا: غالبًا ما تأتي الأبواب الداخلية إما الأبواب الصلبة مقابل الأبواب المجوفة. يعتبر القلب المجوف أخف وزناً وأرخص، بينما يوفر القلب الصلب عزلاً صوتياً أفضل وإحساساً أكثر جوهرية.
ج. ميزات اللوحة الخاصة (إضافة الأناقة والوظيفة)
- التزجيج/الإضاءة: هذه ببساطة ألواح زجاجية داخل الباب. يمكن أن تكون شفافة، أو مصقولة، أو مزخرفة، أو موفرة للطاقة.
- فتحات التهوية: فتحات شبكية (مثل فتحات التهوية) مدمجة في لوحة الباب، وغالبًا ما تُرى على أبواب الخزانة أو غرفة المرافق للسماح بدوران الهواء.
- الحشوات والتفاصيل الزخرفية: قوالب مرتفعة، أو نقوش، أو تفاصيل مطبقة، أو حشوات مواد مختلفة تضيف اهتمامًا بصريًا لوجه اللوحة.
مكونات أجهزة الباب: الأجزاء الوظيفية
الأجهزة هي ما يجعل الباب فعالاً! فهي تسمح بالحركة، وتوفر الأمان، وتزيد من سهولة الاستخدام.
مكونات أجهزة الأبواب
أ. أجهزة الحركة (كيفية تأرجحها أو انزلاقها)
- المفصلات: هذه هي الطريقة الأكثر شيوعًا لفتح وإغلاق الأبواب.
- مفصلات المؤخرة: النوع الأكثر شيوعًا، مع ورقتين متطابقتين (واحدة على حافة الباب، وواحدة على عمود الباب) متصلتين بدبوس.
- المفصلات المستمرة/البيانو: قم بتشغيل طول الباب بالكامل للحصول على دعم قوي.
- مفصلات زنبركية: إغلاق الباب تلقائيًا (غالبًا ما يكون مطلوبًا للأبواب المقاومة للحريق).
- مفصلات محورية: اسمح للباب بالدوران من نقاط في الأعلى والأسفل، بدلاً من الجانب (يستخدم هذا عادةً للأبواب الثقيلة جدًا أو الحديثة).
- أدوات باب الحظيرة: أنظمة المسار والبكرات المكشوفة المثبتة فوق فتحة الباب.
ب. أجهزة القفل والأمان (الحفاظ عليها مغلقة وآمنة)
- مجموعات الأقفال: الآلية الرئيسية للإغلاق والقفل.
- قفل الحفر: صندوق معدني كبير مستطيل الشكل، مُثبَّت في جيب (مِزْرَق) مُقْطَع في حافة الباب. طراز قديم، ولكنه غالبًا ما يكون متينًا جدًا.
- القفل الأسطواني (أو القفل الممل): يُركّب في فتحتين دائريتين محفورتين في واجهة الباب وحافته. شائع الاستخدام اليوم (يشمل المقابض والرافعات القياسية).
- قفل أنبوبي: نسخة أبسط من القفل الأسطواني، تستخدم غالبًا للممرات الداخلية أو وظائف الخصوصية.
- المقابض والرافعات والمقابض: الجزء الذي تُمسكه لفتح الباب. عادةً ما تكون الرافعات أسهل استخدامًا من المقابض، خاصةً لسهولة الوصول.
- أقفال الأبواب: يوفر أمانًا أساسيًا. يمتد البرغي عميقًا داخل دعامة القفل، ويُشغّل بمفتاح أو مفتاح إبهام. منفصل عن آلية القفل الرئيسية.
- لوحات الإضراب: صفيحة معدنية مثبتة على دعامة الباب مزودة بثقب (ثقوب) لتثبيت مزلاج القفل و/أو المزلاج عند إغلاق الباب. تُعزز هذه الصفيحة دعامة الباب وتضمن تثبيتًا سلسًا.
- الأقفال الذكية: أقفال إلكترونية توفر الدخول بدون مفتاح عبر الرموز والتطبيقات وبصمات الأصابع وما إلى ذلك.
ج. الأجهزة الأساسية الأخرى (الإضافات)
- أجهزة إغلاق الأبواب: أجهزة (غالبًا هيدروليكية) تُركّب أعلى الباب/الإطار، وتُغلق الباب تلقائيًا بسرعة مُتحكم بها. شائعة في الأماكن التجارية، وأبواب الحرائق، وأحيانًا أبواب العواصف.
- صفائح الركل: ألواح معدنية مثبتة في الجزء السفلي من لوحة الباب على جانب الدفع لحمايتها من الخدوش والانبعاجات والأوساخ الناتجة عن الأقدام أو العربات.
- لوحات الدفع/السحب: لوحات معدنية مثبتة على الأبواب (غالباً تجارية) تشير إلى مكان الدفع أو السحب، وتتضمن في بعض الأحيان مقبضًا.
- مانعات الأبواب (مثبتة على الحائط/الأرضية): مختلفة عن التوقفات في الإطار! هذه أجهزة صغيرة تُركّب على الحائط أو الأرض خلف الباب لمنع مقبض الباب/الرافعة من الاصطدام بالحائط عند فتح الباب.
- مسامير مسطحة: مسامير منزلقة مثبتة في الحافة (عادةً العلوية والسفلية) غير نشط باب في زوج من الأبواب المزدوجة (مثل الأبواب الفرنسية) لإبقائه مغلقًا.
- المنافذ (فتحات الرؤية): عدسات صغيرة يتم تركيبها من خلال الباب مما يسمح للسكان برؤية الخارج دون فتح الباب.
(تخيل مخططًا منفجرًا هنا: يُظهر مجموعة أقفال مفككة، وأنواعًا مختلفة من المفصلات، ومزلاجًا، ولوحة إضراب، وإغلاقًا، وما إلى ذلك.)
أنواع خاصة من الأبواب ومكوناتها الفريدة
تحتوي أنماط الأبواب المختلفة على أجزاء فريدة:
أنماط ومكونات الأبواب الخاصة
- أ. تشريح الباب الفرنسي: متسائل ما هو الباب الفرنسيعادةً ما يكون زوجًا من الأبواب ذات ألواح زجاجية (لايتس) تُفتح من المنتصف. تشمل أجزاؤها الفريدة ما يلي:
- استراغال: شريط صب عمودي مُثبّت على حافة باب واحد كزوج. يُغطي الفجوة بين البابين عند إغلاقهما، مُوفرًا بذلك سدًا، وفي بعض الأحيان يُؤوي آليات قفل.
- أقفال متعددة النقاط: أنظمة قفل تعمل على تأمين الباب في نقاط متعددة (أعلى، أسفل، وسط) باستخدام مقبض واحد، وهي شائعة في الأبواب الفرنسية الطويلة أو أبواب الفناء من أجل الأمان والختم.
- مسامير مسطحة: كما ذكرنا سابقًا، يتم استخدامه لتأمين الباب غير النشط.
- ب. الأبواب المنزلقة والجيبية والحظيرة والأبواب القابلة للطي: تعتمد هذه الأنظمة على المسارات والبكرات بدلاً من المفصلات.
- أنظمة المسار: قنوات معدنية أو بلاستيكية (مثبتة في الأعلى أو في بعض الأحيان على الأرض) تعمل على توجيه حركة الباب.
- الشماعات/البكرات: عجلات أو حاملات مثبتة في الجزء العلوي من لوحة الباب والتي تتحرك في المسار.
- الأدلة: قطع صغيرة (عادة ما تكون مثبتة على الأرض) تمنع الجزء السفلي من الأبواب المنزلقة/الأبواب الحظيرة من التأرجح من جانب إلى آخر.
- إطارات الجيب: هياكل حائطية مسبقة الصنع مصممة خصيصًا لحمل باب الجيب بشكل أنيق داخل الحائط عند فتحه.
- سحوبات الحافة: مقابض صغيرة غائرة تستخدم على حافة الأبواب الجيبية لاستعادتها من تجويف الحائط.
- محور/محاذاة الأجهزة: يتم استخدام موصلات ومحاور خاصة في الأبواب القابلة للطي للسماح للألواح بالطي بسلاسة والبقاء محاذية.
قياسات ومواصفات الأبواب: لعبة الأرقام
إن الحصول على التفاصيل الصحيحة أمر بالغ الأهمية للأداء السليم.
- أ. الأحجام القياسية: تتوفر الأبواب بأحجام شائعة. معرفة أحجام الأبواب القياسية (مثل ارتفاع ٨٠ بوصة وعرض ٣٠ أو ٣٦ بوصة في الولايات المتحدة) يُسهّل عملية الطلب أو الاستبدال. تُستخدم المقاسات المترية في العديد من أنحاء العالم.
- ب. وضع الأجهزة:
- انتكاسة: المسافة من حافة الباب إلى مركز الفتحة المُثقبة لقفل الباب (عادةً ما تكون المسافة الخلفية ٢ ⅜” و٢ ¾”). تُعدّ هذه المسافة بالغة الأهمية لضمان تثبيت القفل بشكل صحيح.
- حجم التجويف: قطر الثقب (الثقوب) الرئيسي المثقوب لمجموعة القفل/المزلاج. يجب أن يتوافق مع متطلبات الأجهزة.
- تباعد المفصلات والفجوة: يجب تركيب المفصلات بشكل صحيح على طول إطار الباب وحافة الباب. يجب ترك فجوات صغيرة ومتناسقة حول لوحة الباب ليتحرك بحرية دون أي عوائق.
- ج. تسامحات التثبيت: هناك نطاقات مقبولة للفجوات والمسافات حول الباب والإطار لضمان سلاسة التشغيل ونقل الأخشاب موسميًا. قد تحدد قوانين البناء مسافات محددة، خاصةً للأبواب المقاومة للحريق.
- د. التصنيفات والمعايير:
- ANSI/BHMA: ابحث عن الدرجات (مثل الدرجة ١، ٢، ٣) على الأجهزة التي تُشير إلى معايير الأداء والمتانة والأمان التي وضعها المعهد الوطني الأمريكي للمعايير / جمعية مُصنّعي أجهزة البناء. عادةً ما تكون الدرجة ١ هي الأعلى/الأكثر متانة.
- تصنيفات الحرائق: تحتاج الأبواب (والإطارات/الأجهزة) المستخدمة في مواقع محددة (مثل تلك الموجودة بين المرآب والمنزل) إلى تصنيفات مقاومة للحريق (على سبيل المثال، 20 دقيقة، 90 دقيقة) تشير إلى المدة التي يمكنها فيها مقاومة الحريق.
- تصنيفات الصوت (STC): تشير تصنيفات فئة عزل الصوت إلى مدى كفاءة تركيب الباب في عزل الصوت. يعني ارتفاع تصنيف STC عزلًا صوتيًا أفضل.
إمكانية الوصول والمكونات المتخصصة: تلبية الاحتياجات المحددة
تم تصميم بعض المكونات لتلبية متطلبات محددة:
- أ. الميزات المتوافقة مع قانون الأمريكيين ذوي الإعاقة: لتلبية معايير إمكانية الوصول:
- مقابض الرافعة مطلوبة بدلاً من المقابض المستديرة (أسهل في الإمساك).
- العتبات يجب أن يكون منخفض الارتفاع (ارتفاعه الأقصى ½ بوصة، وغالبًا ما يكون مشطوفًا).
- غلق الأبواب يجب أن تعمل ببطء كافٍ حتى لا تعيق المرور.
- الحد الأدنى عرض الفتح واضح (عادةً ما يكون 32 بوصة) يجب توفيرها.
- ب. مكافحة الحرائق والصوت:
- الأختام المنتفخة: شرائط خاصة يتم تطبيقها على الأبواب/الإطارات المقاومة للحريق والتي تنتفخ بسرعة عند تعرضها للحرارة، مما يؤدي إلى سد الفجوات لمنع الدخان واللهب.
- الزجاج المقاوم للحريق: زجاج تم اختباره لتحمل الحريق لفترة محددة.
- النوى الصوتية: مواد كثيفة داخل لوحة الباب مصممة لمنع الصوت.
- الأختام الصوتية والكاسحات: أختام عالية الأداء حول الإطار وأسفل الباب مصممة خصيصًا لتقليل الصوت إلى أقصى حد.
- ج. كفاءة الطاقة:
- النوى المعزولة: رغوة أو مواد عازلة أخرى داخل لوحة الباب (مهمة بشكل خاص للأبواب الخارجية) لتقليل انتقال الحرارة (يتم قياسها من خلال قيمة R أو عامل U).
- عوازل الطقس والكنس عالية الأداء: تأكد من إحكام الغلق لمنع تسرب الهواء.
استكشاف الأخطاء وإصلاحها حسب المكون: إصلاح المشكلات الشائعة
معرفة الأجزاء تساعد في تشخيص المشكلات:
- "بابي يلتصق أو يقيد."
- يفحص: المفصلات (مسامير فضفاضة، دبابيس مثنية، مهترئة؟)، لوحة الباب (منتفخة بسبب الرطوبة؟)، الإطار (مستقر، خارج المربع؟).
- حل: قم بربط البراغي، ومفصلات الدعامات، وتسوية حافة الباب قليلاً، وضبط الإطار إذا كان ذلك ممكنًا.
- "الباب لن يغلق بشكل صحيح."
- يفحص: محاذاة مزلاج القفل مع فتحة لوحة الضربة، وموضع لوحة الضربة، ومحاذاة المفصلة (الباب المترهل؟).
- حل: قم بضبط موضع لوحة الضربة (فتح الملف بشكل أوسع أو إعادة وضعه)، ومفصلات الحشو لإعادة محاذاة الباب.
- "هناك تيار هوائي حول الباب."
- يفحص: شرائط الطقس (مهترئة، مضغوطة، مفقودة؟)، عوازل الأبواب (مهترئة، تالفة، اتصال ضعيف؟)، سدادات الأبواب (هل يغلق الباب بإحكام ضدها؟).
- حل: استبدال شرائط الطقس/المسح، وضبط التوقفات أو المزلاج للحصول على إغلاق أكثر إحكامًا.
- "القفل صعب الفتح أو يلتصق."
- يفحص: هل المفتاح تالف؟ آلية القفل بحاجة إلى تزييت؟ هل البرغي غير محاذٍ للوحة القفل؟
- حل: جرب استخدام مادة التشحيم الجرافيتية (وليس الزيت!)، وتحقق من المحاذاة، فقد تكون هناك حاجة إلى استبدال مجموعة القفل.
افعلها بنفسك مقابل الاستبدال: غالبًا ما تُجرى التعديلات البسيطة (مثل شد البراغي، والتشحيم، واستبدال العوازل) يدويًا. أما التعديلات الأكثر تعقيدًا (مثل تسوية الأبواب، وإعادة وضع ألواح الشد بشكل ملحوظ، واستبدال أقفال المفصلات) فقد تتطلب مهارة أكبر أو مساعدة متخصصة.
اختيار مكونات الباب المناسبة: اتخاذ خيارات ذكية
عند الشراء أو الترقية، ضع في اعتبارك ما يلي:
- أ. المواد والمتانة: قارن بين الخشب والألياف الزجاجية والفولاذ والمركبات بناءً على مناخك وميزانيتك ومستوى الصيانة المطلوب. (راجع القسم الرابع (ب) والأدلة المرتبطة به). ما هي مدة بقاء المنتج؟ وما مدى تآكله؟
- ب. مطابقة الأنماط: اختر تصاميم الألواح، وتشطيبات الأجهزة، وأنماط التغليف التي تُكمّل هندسة منزلك (تقليدي، حديث، ريفي، إلخ). التناسق مهم!
- ج. الوظائف والأداء وكفاءة الطاقة:
- حماية: إعطاء الأولوية للمزالج القوية والأبواب الصلبة أو المعدنية للوصول إلى الخارج.
- التحكم في الصوت: اختر الأبواب ذات القلب الصلب والأختام الجيدة بين الغرف إذا كان الضوضاء مصدر قلق.
- توفير الطاقة: أمر بالغ الأهمية للأبواب الخارجية - ابحث عن أنوية معزولة وعوازل/ممرات جوية ممتازة.
- سهولة التثبيت: بالنظر إلى ما هو الباب المعلق مسبقًا؟ يمكن أن توفر الوحدة (الباب الموجود بالفعل في إطاره) وقتًا وجهدًا كبيرين في التركيب مقارنة بتثبيت باب لوح.
مسرد شامل لمصطلحات الأبواب
لقد غطينا العديد من المصطلحات! هذا الدليل بأكمله بمثابة مسرد، ولكن إليك بعض المصطلحات الرئيسية باختصار:
- عضادة: الأجزاء الجانبية العمودية لإطار الباب.
- العضادة: قطع الحافة الهيكلية العمودية للوحة الباب نفسها.
- السكك الحديدية: القطع الهيكلية الأفقية للوحة الباب.
- قف: الشريط الموجود داخل الإطار الذي يغلق عليه الباب.
- غلاف: الزخرفة الزخرفية حول الإطار.
- لوحة الإضراب: اللوحة المعدنية الموجودة على عمود الباب والتي تمسك المزلاج/البرغي.
- انتكاسة: القياس من حافة الباب إلى مركز فتحة القفل.
- معلق مسبقًا: وحدة باب تباع مع اللوحة المثبتة بالفعل في الإطار.
- بلاطة: فقط لوحة الباب نفسها، بدون إطار أو أجهزة.
الخاتمة والموارد الإضافية
وها قد انتهينا! رحلةٌ عميقةٌ في عالم قطع الأبواب. أرأيتم؟ الأمر ليس مخيفًا!
النقاط الرئيسية:
- الباب عبارة عن نظام: الإطار، واللوحة، والأجهزة، والأجزاء الزخرفية كلها تعمل معًا.
- إن معرفة أسماء الأجزاء (مثل العوارض، والقضبان، والعتبات، وألواح الإضراب) تساعدك على فهم كيفية عمل الأبواب، وإصلاح المشكلات، والاختيار بحكمة.
- تؤثر المواد (الخشب والألياف الزجاجية والصلب) ونوع القلب (صلب/مجوف) وجودة الأجهزة بشكل كبير على الأداء والمتانة والأمان.
- تحتوي الأبواب الخاصة (الفرنسية، والمنزلقة، وما إلى ذلك) على مكونات فريدة تحتاج إلى معرفتها.
- تعتبر القياسات والمواصفات (مثل الحجم الخلفي والأحجام القياسية) ضرورية للملاءمة والوظيفة المناسبة.
إن فهم هذه المكونات يمكّنك من صيانة منزلك بشكل أفضل، واتخاذ قرارات مستنيرة أثناء عمليات التجديد، وتقدير الهندسة الذكية في شيء بسيط مثل الباب!
نأمل أن يكون هذا الدليل قد فتح الباب (وهذا من باب التورية!) لفهم أفضل لجميع هذه الأجزاء الأساسية. بالتوفيق في مشروعك القادم!










